-d = Database name
-i = Write your SQL script in this file.
-o = If you want the SQL query output to be stored in a separate file.
If you have been working with SQL Server Management Studio, you know that you can execute any sql query by selecting it and then press F5. That’s a manual work and you have to execute the query to get the desired output. Let’s say that you want to automate these part and the you have a lot of ad-hoc query in a file and that has to be executed. There is a
sqlcmd utility to execute queries within command prompt. So in this post, we will first see how to connect to the database and execute few queries interactively and execute SQL queries stored in a file.
Okay, let’s start.
Open command prompt in windows and then enter sqlcmd then press Enter.
Now you will see 1> and if you press Enter once again the number will increment to 2>.

exit()

sqlcmd utility executes all the sql queries in the batch. The batch is identified based on the batch separator. This is how you can execute the query.
1> and waiting for another query to be entered. This is in interactive mode.



sqlcmd utility has connected to the local sql server instance using trusted connection (i.e., Windows authentication) and returned the result.
If you want to specify the detail explicitly, you can do like below.-S (uppercase) - to specify the server name. I am connecting from a laptop where SQL Server is installed locally. So I have to connect to the
localhost. You can also use . (dot) or 127.0.0.1 IP address to represent the local host server.


-E.

SQL-VM and SQL Server instance installed in that server is SQL2019, you should use SQL-VM\SQL2019 instead of localhost .

-d (lowercase).
-d - database name

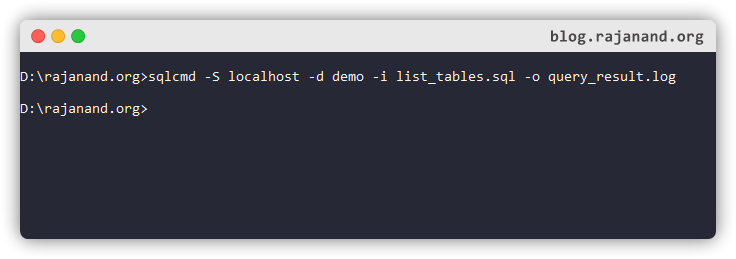
list_tables.sql in the same directory D:\rajanand.org\
-i - to specify an input file.

sqlcmd utility takes the SQL file as an input and executes the query but displays the output result in command prompt itself. Similarly how we have changed the input SQL query to a file, we will do the same for output. This way we will have output message stored in the file for future reference.
Let us change that to insert into a separate file.
-o (lowercase o )


sqlcmd command within a batch file (.bat) and then execute the batch file.

sqlcmd utility accepts, try sqlcmd -?

Summary
You have learned to- Execute query within command prompt
- Execute sql file within command prompt
- Execute query and save output to a file.
- Get user input for server and database name and execute the sql file connecting to that database.