
Basics
PowerShell is a command-line shell and scripting language that is designed to help you automate administrative tasks. With PowerShell, you can automate repetitive tasks, manage remote computers, and perform complex operations on data. To open PowerShell, click on the Start button and type in “PowerShell” in the search box. You can also open PowerShell from the Command Prompt by typing in “PowerShell” and hitting Enter. You can also open PowerShell in Windows Terminal. Once you have PowerShell open, you can start typing in commands.How to Set Up PowerShell Properly
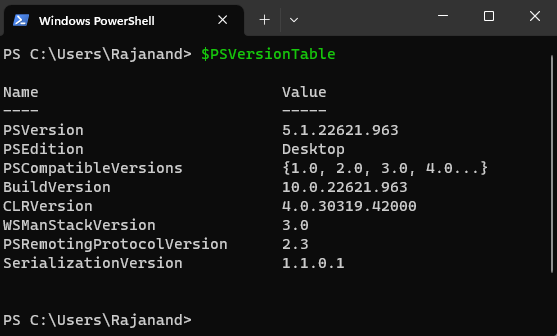
In this post, we’ll cover the basics of setting up PowerShell on your machine. We’ll go over the different versions of PowerShell, how to check which version you have, and how to install or update PowerShell if necessary. We’ll also cover how to configure PowerShell to run scripts and how to set execution policies. If you’re new to PowerShell, the first thing you need to do is set it up on your machine. PowerShell comes pre-installed on most Windows machines, but if you need to install or update PowerShell, it’s a straightforward process. First, you need to determine which version of PowerShell you have installed on your machine. To do this, open PowerShell and type in$PSVersionTable. This will display the version of PowerShell you have installed, along with some other useful information.
 PowerShell is by default, installed in all windows versions. But, If you need to install or update PowerShell, you can download the latest version from the Microsoft website.
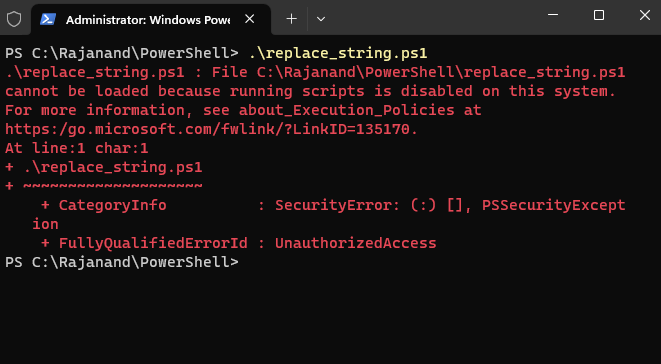
After you’ve installed PowerShell, you may need to configure it to run scripts. By default, PowerShell restricts the execution of scripts to prevent malicious code from running on your machine. You will get the below error if you try to run a script.
Error: File
PowerShell is by default, installed in all windows versions. But, If you need to install or update PowerShell, you can download the latest version from the Microsoft website.
After you’ve installed PowerShell, you may need to configure it to run scripts. By default, PowerShell restricts the execution of scripts to prevent malicious code from running on your machine. You will get the below error if you try to run a script.
Error: File C:\powershell_filename.ps1 cannot be loaded because running scripts is disabled on this system.
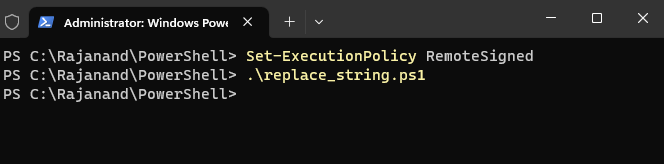
 To allow the script to run, you need to set the execution policy. To do this, open PowerShell as an administrator and type in
To allow the script to run, you need to set the execution policy. To do this, open PowerShell as an administrator and type in Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned.
 PowerShell commands are called cmdlets (“Command-Lets” and they follow a verb-noun syntax. For example, to list the contents of a directory, you would use the
PowerShell commands are called cmdlets (“Command-Lets” and they follow a verb-noun syntax. For example, to list the contents of a directory, you would use the Get-ChildItem cmdlet.
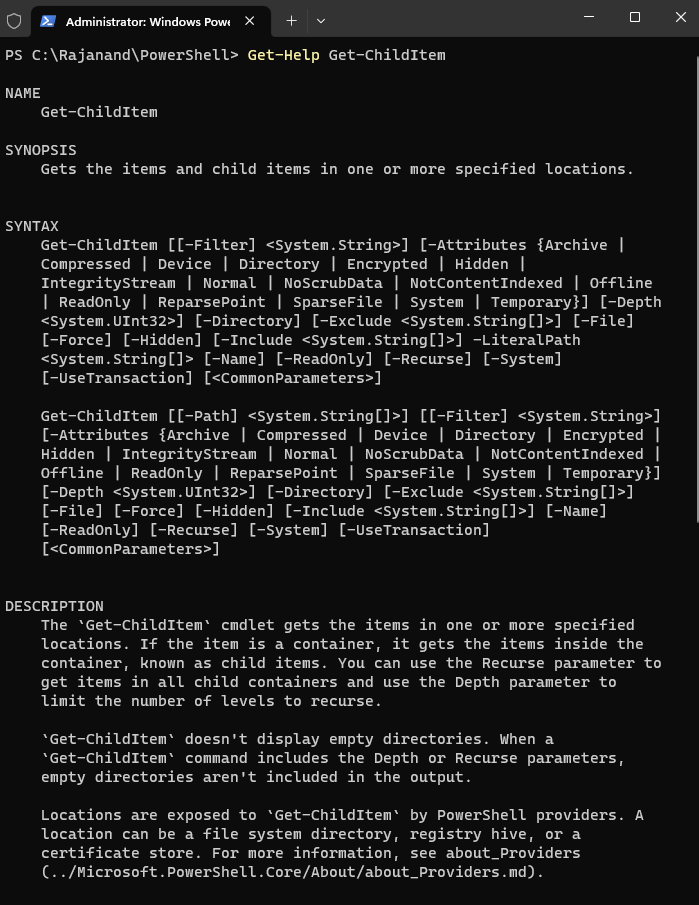
How to get-help?
To get help with a cmdlet, you can use theGet-Help cmdlet.
 One of the most powerful features of PowerShell is its ability to interact with other applications. For example, you can use PowerShell to manage SQL Server, Azure, Exchange Server, and SharePoint. PowerShell also supports .NET Framework classes and methods, which means you can use PowerShell to work with a wide range of Windows applications.
In summary, we have seen how to check the PowerShell version and how to get help. In the next post, we will explore variables. Thanks for reading this far and we are ready to start the PowerShell adventure. If you have any questions, feel free to ask away in the comment section.
One of the most powerful features of PowerShell is its ability to interact with other applications. For example, you can use PowerShell to manage SQL Server, Azure, Exchange Server, and SharePoint. PowerShell also supports .NET Framework classes and methods, which means you can use PowerShell to work with a wide range of Windows applications.
In summary, we have seen how to check the PowerShell version and how to get help. In the next post, we will explore variables. Thanks for reading this far and we are ready to start the PowerShell adventure. If you have any questions, feel free to ask away in the comment section.
variables
Like any other programming language, variables are used to store values and data. They can be used to store text, numbers, objects, and other data types. Variables in PowerShell are denoted by a dollar sign ($), followed by the name of the variable. E.g.,$name is variable.
To create a variable in PowerShell, simply type the name of the variable, followed by the equals sign (=), and the value you want to assign to the variable. For example, to create a variable called $name and assign it the value “Raj”, you would type:
$name variable, you would type:
$name variable, you could use the following command:
$name variable to “Anto”, you would type:
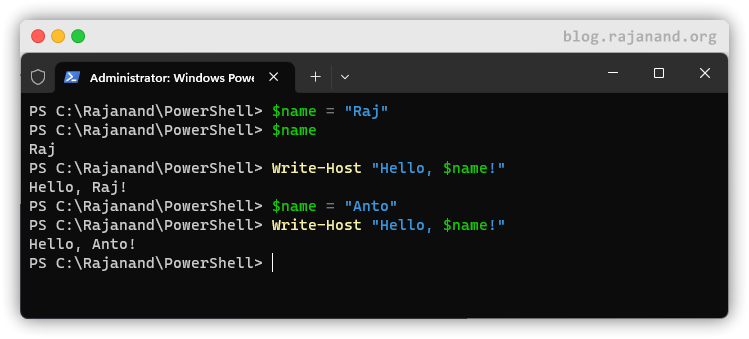 In PowerShell, variables can also be used in combination with other commands and functions. For example, you can use variables to specify file paths or database names when working with PowerShell cmdlets.
To summarize, variables are a key concept in PowerShell and are used to store and manipulate data. They are easy to create and use, and can be combined with other commands and functions to perform powerful operations.
In PowerShell, variables can also be used in combination with other commands and functions. For example, you can use variables to specify file paths or database names when working with PowerShell cmdlets.
To summarize, variables are a key concept in PowerShell and are used to store and manipulate data. They are easy to create and use, and can be combined with other commands and functions to perform powerful operations.
PowerShell Cmdlets and Alias
In the previous post, we covered variables in PowerShell. In this post, we will be discussing cmdlets. It is pronounced as “command-lets.” It is the fundamental building block of PowerShell. It is a small, single-purpose, lightweight command that performs a specific task. It is designed to be used in combination with other cmdlets to accomplish complex tasks. PowerShell includes hundreds of built-in cmdlets for tasks such as managing the file system, managing services, and managing processes. Additionally, many third-party software vendors provide PowerShell cmdlets for their products, including Microsoft SQL Server. Cmdlets have a consistent naming convention of Verb-Noun, where the verb describes the action to be taken, and the noun describes the object the action is being taken on. For example, the cmdlet for creating a new folder isNew-Item, where “New” is the verb, and “Item” is the noun.
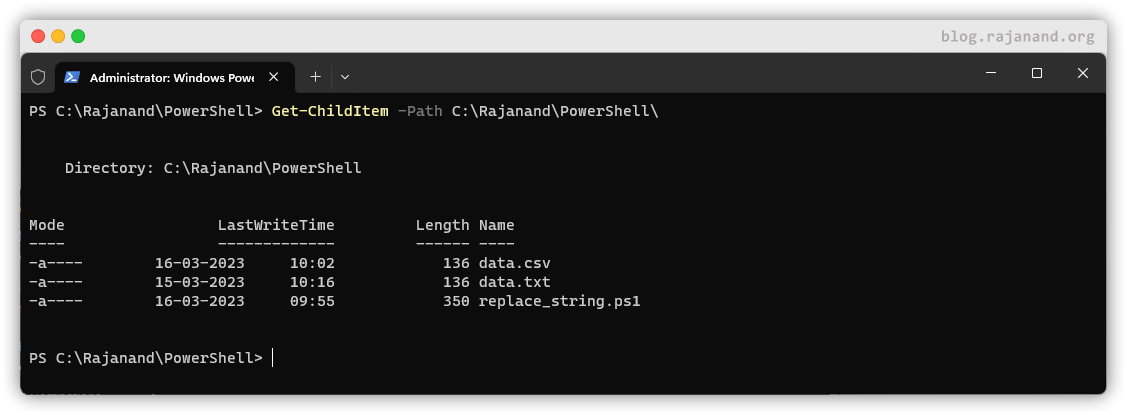
To use a cmdlet, simply type its name followed by any required parameters. Let’s take a look at an example using the Get-ChildItem cmdlet:
Get-ChildItem cmdlet is used to retrieve a list of all items in the C:\Rajanand\PowerShell\ folder.
 Cmdlets can also be piped together to perform more complex tasks. For example, let’s say we wanted to find all files in the folder whose file name starts with
Cmdlets can also be piped together to perform more complex tasks. For example, let’s say we wanted to find all files in the folder whose file name starts with data. We could use the Get-ChildItem and Where-Object cmdlets together like this:
Get-ChildItem cmdlet to retrieve a list of all items in the C:\Rajanand\PowerShell\ folder. We then pipe(i.e., |) that list to the Where-Object cmdlet, which filters the list to only include items with a Name property starts with data.

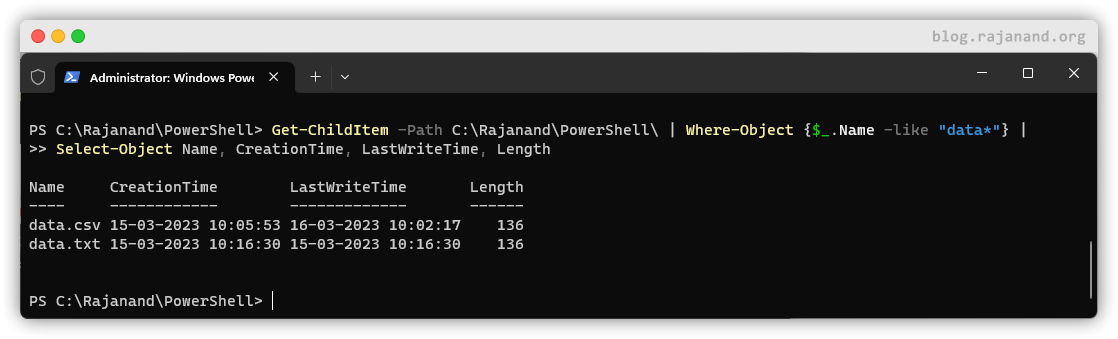 Finally, we pipe the filtered list to the
Finally, we pipe the filtered list to the Select-Object cmdlet, which selects and displays only the Name, CreationTime, LastWriteTime and Length properties of the remaining items.
Alias
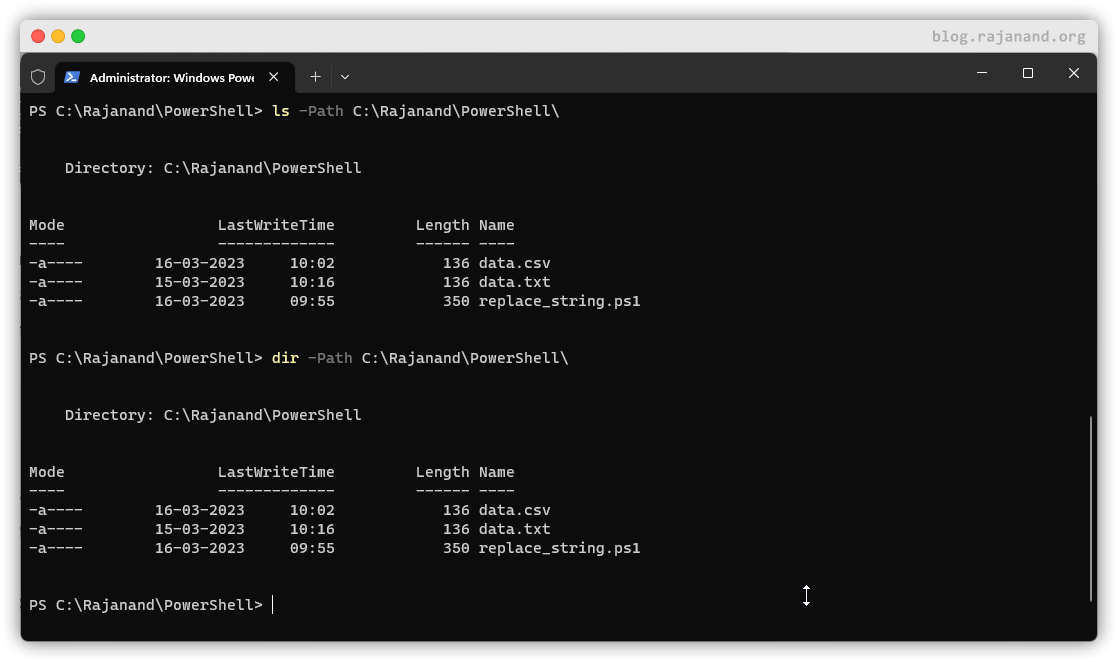
It’s worth noting that many cmdlets also have aliases, which are shorter or alternative names for the same cmdlet. For example, theGet-ChildItem cmdlet has an alias of ls or dir . ls is used in Unix based system to list out the files in the current directory and dir is used in windows for the same purpose.
As you can see below, We are able to get the list of items in a directory using ls and dir alias of Get-ChildItem
 If you want to know about all the alias defined, you can get the same using the cmdlets
If you want to know about all the alias defined, you can get the same using the cmdlets Get-Alias
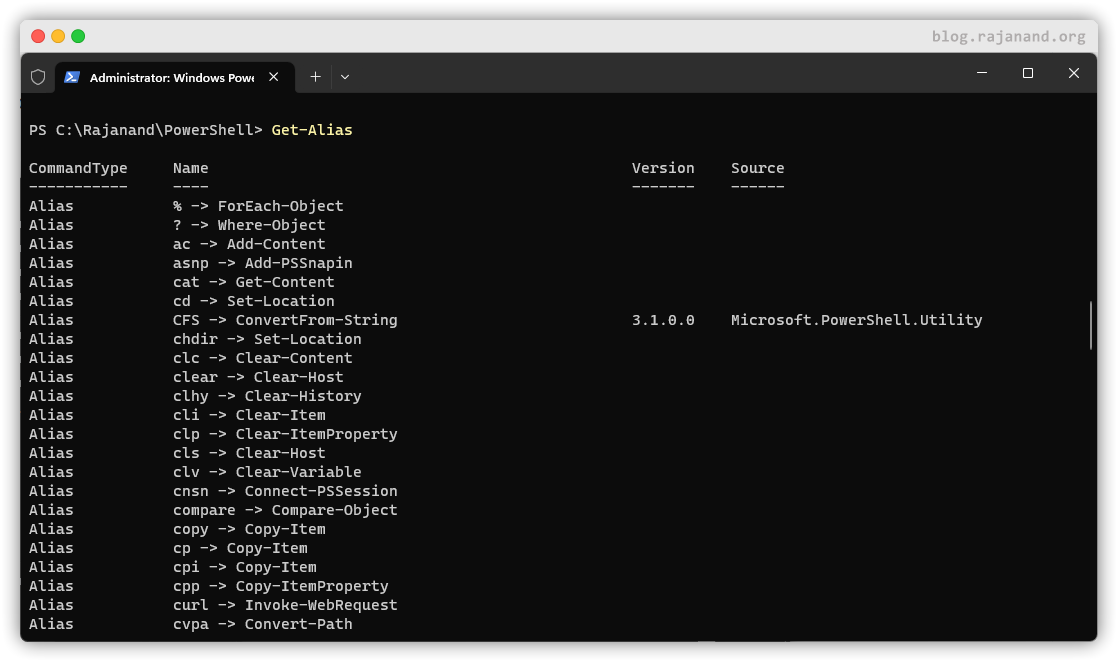 Similary, If you want to set an alias for any of the cmdlets that you use frequently, then you can achieve the same using
Similary, If you want to set an alias for any of the cmdlets that you use frequently, then you can achieve the same using Set-Alias
In conclusion, cmdlets are the basic building blocks of PowerShell and provide a powerful and flexible way to perform a wide range of tasks. Alias is used to simplify the command that we frequently use.